We often use integrals of the functions  , for various values of p, to help determine whether other integrals converge or diverge.
, for various values of p, to help determine whether other integrals converge or diverge.
You already did the work to show this, so we'll just summarize the results. Assuming p is greater than 0 (because otherwise the exponents do weird things),
 converges if p < 1 and diverges otherwise.
converges if p < 1 and diverges otherwise. converges if p > 1 and diverges otherwise.
converges if p > 1 and diverges otherwise.
This is often called the p-test for improper integrals.
Exercise 1
Use the p-test to determine if the integral converges or diverges.

Exercise 2
Use the p-test to determine if the integral converges or diverges.

Exercise 3
Use the p-test to determine if the integral converges or diverges.

Exercise 4
Use the p-test to determine if the integral converges or diverges.


 where p > 1 and the interval of integration is [0,1], this integral diverges.
where p > 1 and the interval of integration is [0,1], this integral diverges.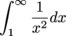
 gets close to the x-axis quickly as x approaches ∞. If you can remember this, then you can remember that
gets close to the x-axis quickly as x approaches ∞. If you can remember this, then you can remember that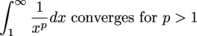
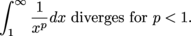
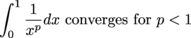
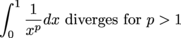
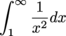

 with p > 1 and we're integrating from 0 to 1.
with p > 1 and we're integrating from 0 to 1.
 with p < 1, so this integral converges.
with p < 1, so this integral converges.
 with p > 1 and we're integrating from 1 to ∞.
with p > 1 and we're integrating from 1 to ∞. is of the form
is of the form