ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Test Prep Videos 443 videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
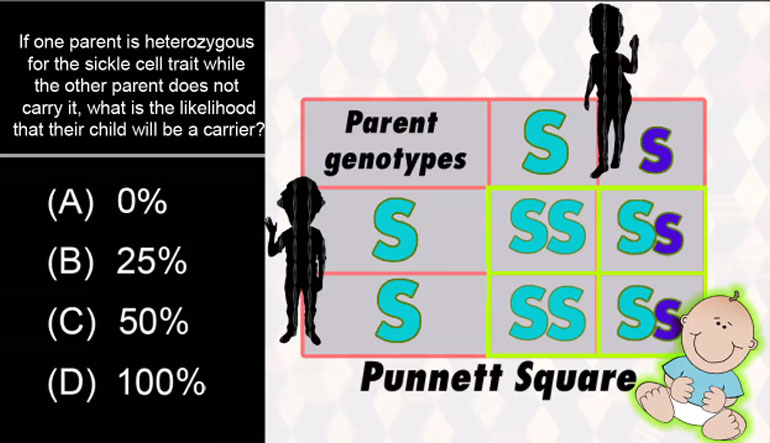
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
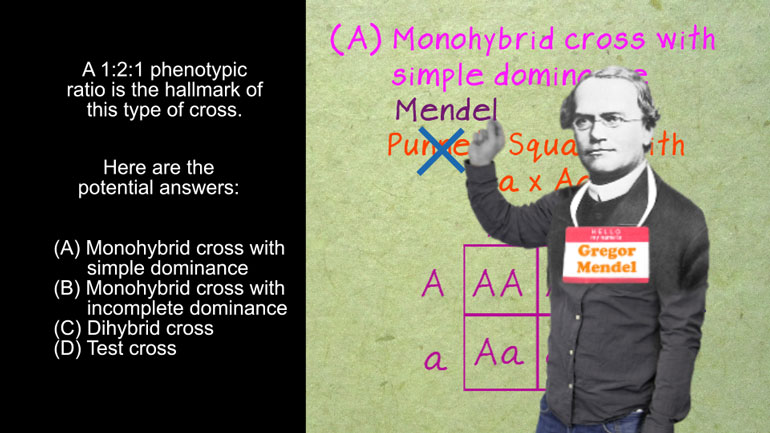
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Bio 3.4 Evolution 50 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Bio 3.4 Evolution. What does gene flow do?
Transcript
- 00:03
Here’s your shmoop du jour, brought to you by gene flow.
- 00:07
It has nothing to do with how awesomely your skinny jeans fit. [Girls in dressing room]
- 00:11
Gene flow does…what?
- 00:13
And here are the potential answers…
- 00:18
Gene flow is like dandelions being blown into your neighbor’s yard because you napped [Person napping on a hammock]
Full Transcript
- 00:23
instead of mowing the lawn like you promised.
- 00:25
When genes migrate, stuff usually…happens.
- 00:28
However, most DNA mutations occur naturally and not because of gene flow. [Man transforms into the Hulk]
- 00:34
When a cell divides, it makes a copy of the DNA.
- 00:36
It’s not entirely like “cut and paste”.
- 00:40
More like “keep your fingers crossed” and hope for a perfect copy. [Girl crossing her fingers]
- 00:44
Otherwise, you have a mutation.
- 00:47
Gene flow is not the culprit here.
- 00:49
So…
- 00:50
Answer “A’ is wrong.
- 00:51
How about “B”?
- 00:52
Well, in the case of human organisms, we normally select mates on a non-random basis… based [Girl flirts with guy sat on a bench]
- 00:57
instead on easily observable traits.
- 00:59
Fortunately, as we mature, more thought will go into the non-random selection process.
- 01:04
It’s all about the vibes.
- 01:05
And not gene flow.
- 01:06
“B” is incorrect.
- 01:08
With natural selection, certain phenotypes are better able than others to contribute [Man bench pressing]
- 01:13
their genes to the next generation.
- 01:14
They’re more fit and uh…pumped up for action. [People working out in a gym]
- 01:18
The end result is a gradual change in the gene frequencies of that population.
- 01:23
None of which is caused by gene flow.
- 01:25
“C” is out.
- 01:26
As for “D”, gene flow is the transfer of alleles from one population to [Alleles transfer from one circle to another]
- 01:31
another.
- 01:32
This transfer knocks the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium out of whack, because it could change the
- 01:37
allelic frequencies.
- 01:38
And, when those frequencies are the least bit disrupted…well, prepare for some potentially
- 01:43
hairy moments. [Man transforms into a caveman]
- 01:44
“D” is definitely the correct answer.
- 01:46
A word to the wise: you may want to avoid the…deep end of the gene pool… [Man jumps into deep end of a gene pool]
Related Videos
AP Biology: Biological System Interactions Drill 1, Problem 1. Complete the sentence about a saturated fatty acid.
AP Biology: Essential Life Process Information Drill 1, Problem 1. If one parent is heterozygous for the sickle cell trait while the other par...
AP Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 1. The first cells on planet Earth were likely what?
AP Biology: Free Energy and Molecular Building Blocks Drill 1, Problem 1. Which statement incorrectly describes the properties of water?
AP® Biology: Evolution Drives the Diversity and Unity of Life Drill 1, Problem 2. What was likely the first genetic material?