ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Probabilistic Reasoning Videos 17 videos
SAT Math: Statistics and Probability Drill 1, Problem 2. If the four largest numbers in the set were doubled, what would happen to the median...
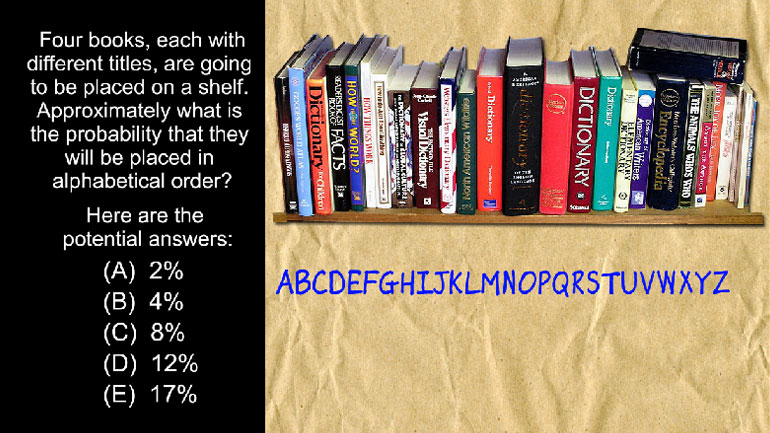
SAT Math 1.3 Statistics and Probability. Approximately what is the probability that they will be placed in alphabetical order?
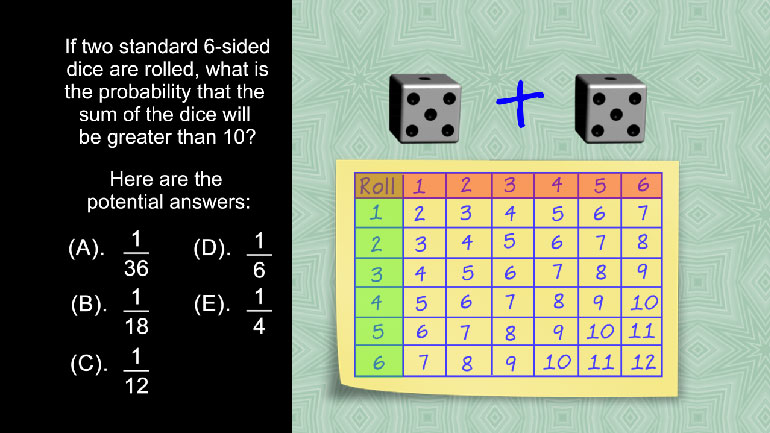
SAT Math 1.4 Statistics and Probability. If two standard 6-sided dice are rolled, what is the probability that the sum of the dice will be gre...
TSI Math: Using Combinations to Select Pizza Toppings 23 Views
Share It!
Description:
What would we need to use to find the number of ways we could pick 3 toppings for a pizza given 10 choices?
- Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability / Probabilistic Reasoning
- Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability / Probabilistic Reasoning
- TSI Math / Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability
- Test Prep / TSI
- TSI Mathematics / Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability
- TSI / TSI Math
- TSI / TSI Mathematics
- Test Prep / TSI
Transcript
- 00:02
Okay sy match members last section in this lovely exam
- 00:06
Ok well here we go What would we need to
- 00:08
use to find the number of ways we could pick
- 00:10
three toppings for a pizza given ten choices Yeah all
- 00:20
right Well when we're picking a smaller group from a
Full Transcript
- 00:22
larger one like the three toppings we want from that
- 00:25
ten topping choices were often trying to determine how many
- 00:28
ways we can pick the smaller group The issue we
- 00:31
have to deal with before we can find the actual
- 00:33
different number of ways to choose our smaller group is
- 00:36
whether the order we choose the items in the smaller
- 00:40
group matters like think about it If you were picking
- 00:43
from a deck of cards the size of that debt
- 00:45
goes from fifty two to fifty one fifty forty nine
- 00:48
so the odds then change on the margin each time
- 00:50
you make a pick So if the order we picked
- 00:53
the items in this problem in the smaller group matters
- 00:56
will end up with loads more options than we will
- 00:58
then if the order doesn't matter if order does matter
- 01:02
like we chose pepperoni green olives and pineapple as our
- 01:05
three well we can also choose green olives pepperoni and
- 01:09
pineapple or pineapple green olives and pepperoni And so on
- 01:13
each of those different ordering sze of the same three
- 01:16
ingredients would be a whole new option We call these
- 01:19
permutations the shortcut simple is npr where n is the
- 01:24
size of the large group and our is the size
- 01:27
of the smaller group and p is well just probability
- 01:31
of what's going on there If order doesn't matter well
- 01:34
then we just get the one option with those three
- 01:36
toppings To get a new option we'd need to toss
- 01:38
out a topping the pineapple get rid of that on
- 01:40
a pizza what they're doing and replace it with something
- 01:43
else like black olives Yeah we call these combinations The
- 01:46
shortcut symbol is n c r where ends the size
- 01:49
of the large group and ours the size of the
- 01:52
small group it's pretty clear order doesn't matter in this
- 01:55
case as it doesn't matter if we choose pepperoni before
- 01:58
green olives or after they all end up in the
- 02:01
same slice and you know in the same place since
- 02:04
this is a combination will need the symbol ten c
- 02:07
three to represent all of our different three items pizzas
- 02:11
so that's it that's the answer at sea Ten c
- 02:13
three
Related Videos
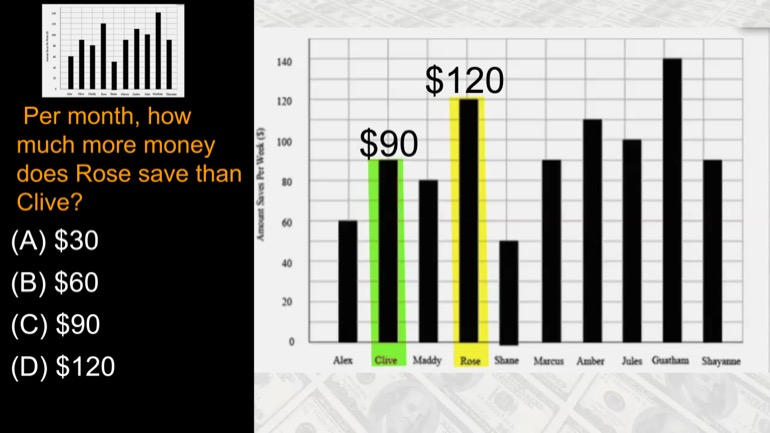
Per month, how much more money does Rose save than Olive?
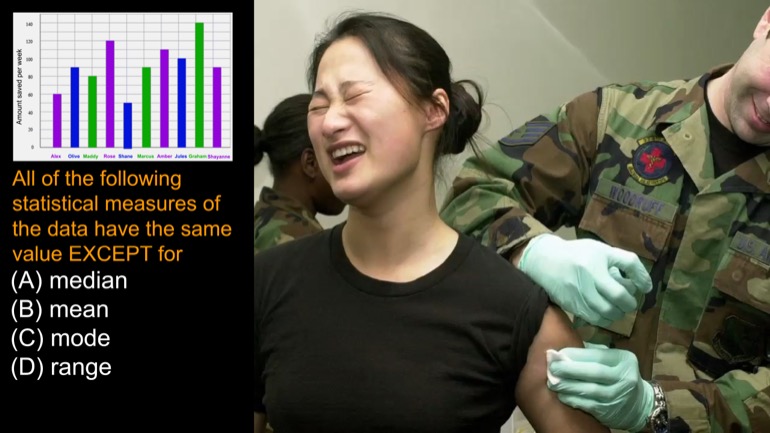
All of the following statistical measures of the data above have the same value EXCEPT for
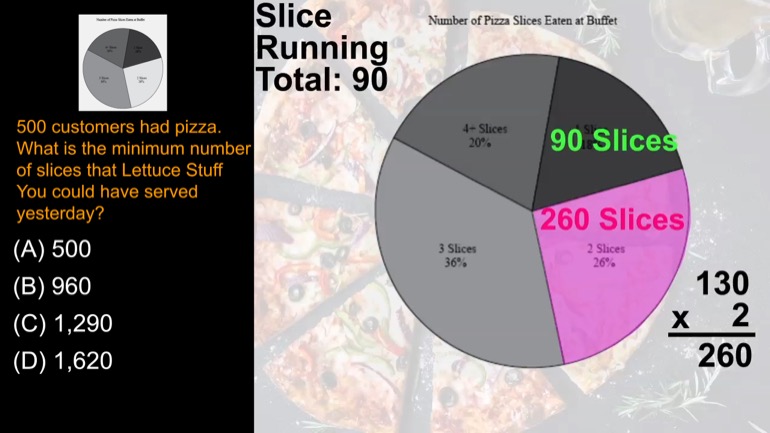
500 customers had pizza. What is the minimum number of slices that Lettuce Stuff You could have served yesterday?
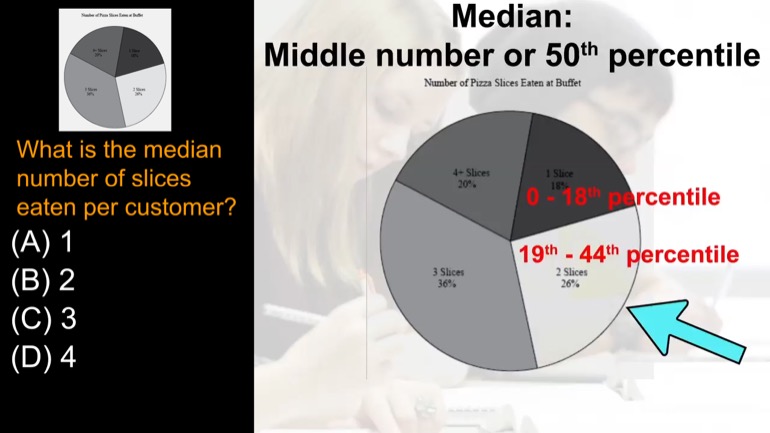
What is the median number of slices eaten per customer?
The following table shows the coffee preferences of everyone in Isabelle's office. What percentage of Isabelle's coworkers put cream in their coffee?