ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Computer Science Videos 112 videos
Just as you move your furniture into a new house before spending the night, you’ve got to spend a little time setting up your environment when yo...
Doubles and ints. At first glance, it may look like this video will be about baseball and football statistics. But they're actually computer scienc...
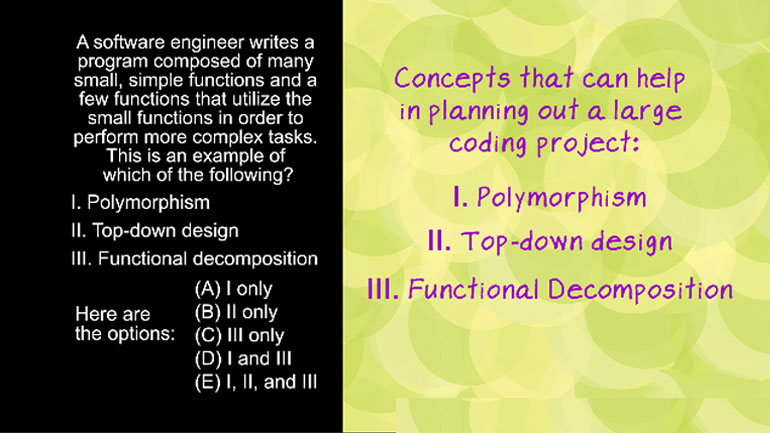
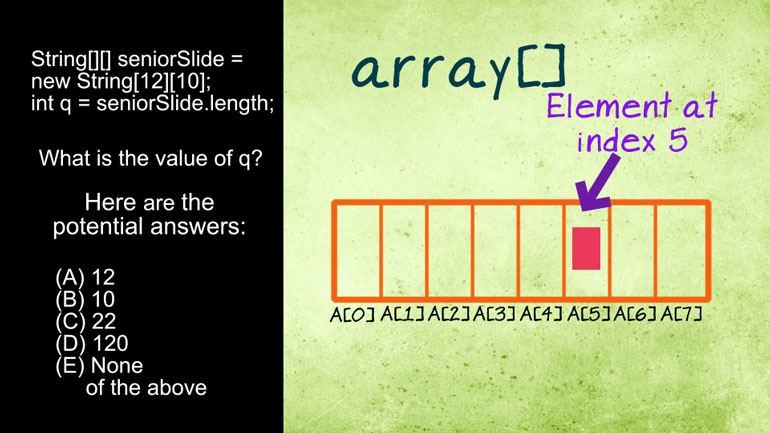
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 1.1 Review of the Basics 315 Views
Share It!
Description:
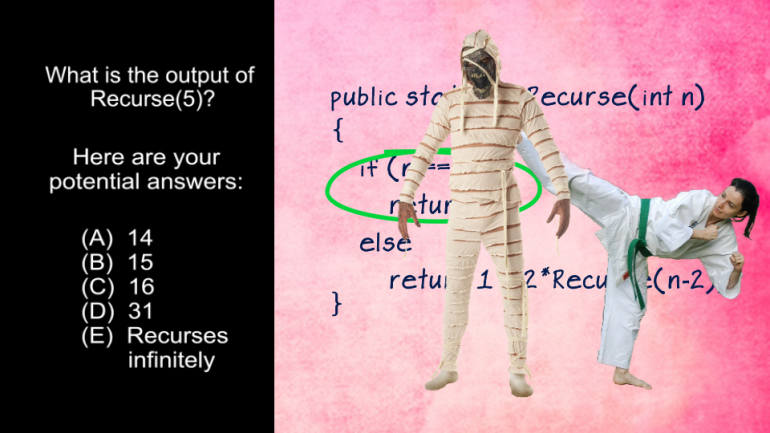
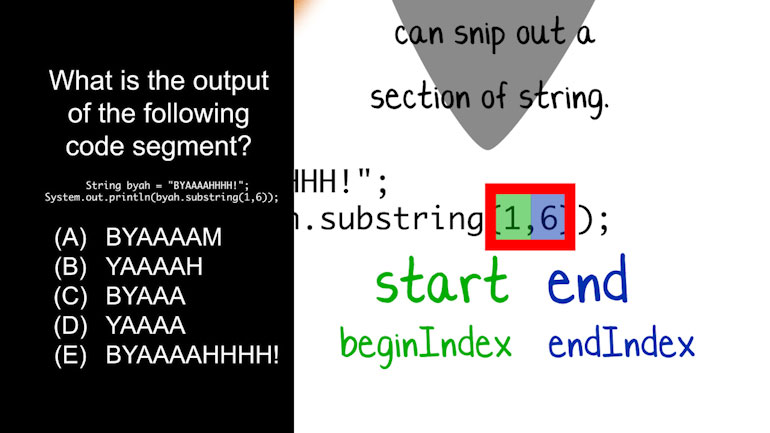
AP Computer Science: Review of the Basics Drill 1, Problem 1. What does this piece of code output?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your shmoop du jour
- 00:05
brought to you by loops Have you coming back time
- 00:09
and time again Little snippet of code for what does
- 00:13
this piece of code right here what is it output
- 00:20
on here The potential answers All right here we go
Full Transcript
- 00:29
Pretty simple Request We just have to prove to the
- 00:33
test and to ourselves that we know how to read
- 00:35
java code and figure out what it does Well it's
- 00:38
Not merely a pest problem This kind of thing is
- 00:41
done all the time when debugging program right but also
- 00:45
comes up quite a bit when software engineers have to
- 00:47
maintain or update pulled code Occasionally you'll have to work
- 00:53
with stuff that had been written five or ten years
- 00:55
ago or more perhaps by someone who is no longer
- 00:57
on the project and maybe they didn't leave comments in
- 01:00
the code so it's tough to figure out exactly what
- 01:02
it was meant to do or they thought they were
- 01:05
being really cute and they left their comments and cling
- 01:08
on Well good luck with that Anyway in this case
- 01:12
is just eight lines but we can already see that
- 01:14
there are a couple of loops that end up doing
- 01:16
an awful lot in that short space So let's go
- 01:19
through and decode this baby step by step All right
- 01:23
up top line one sets us up with manager i
- 01:27
with a value of five Go ahead and write that
- 01:29
down somewhere Scratch paper in your arms whatever we want
- 01:33
to keep track of where this variable takes us Line
- 01:35
two initiates a wild loop which will run as long
- 01:39
as an injured eye remains greater than zero so it's
- 01:42
five now and so it looks like we're good to
- 01:44
go Line three homeboy line three starts another loop nested
- 01:49
inside the first one and this time it's A four
- 01:52
loop Well four loops have three parameters The first being
- 01:55
the initialization imager J is one which is what we'll
- 01:58
be using is the eatery So write that on your
- 02:01
arm or whatever too The second is the termination parameter
- 02:07
When this condition is false the loop will no longer
- 02:10
run Yes j No longer being less than or equal
- 02:13
to I will stop the looting The third parameter is
- 02:19
called the increments and living up to its name It'll
- 02:23
increments j by one Each time the loop cycles Line
- 02:27
four is inside the loop It friends the product of
- 02:30
three times j and its base and he'll do it
- 02:34
over and over and over over within this loop until
- 02:38
j is no longer less than or equal to ay
- 02:42
well first time it runs Jay is one so we
- 02:45
print the product of three times one in a space
- 02:48
Then it'll increase j by one and a loop will
- 02:50
run again so next time it'll be three times too
- 02:53
and a space and then three times three and space
- 02:56
and three times for anna's face and three times five
- 02:59
in space And now jay six which is greater than
- 03:03
i look at your arms eyes five at the moment
- 03:06
That's the necessary condition for our four loop determining through
- 03:10
the chapel So now we move on to what happens
- 03:13
after the four loop which is an empty print line
- 03:16
statement that'll give us a new line and we subtract
- 03:19
one from i you all right But we're not done
- 03:24
The wild loop is still running And this time i
- 03:29
is for the interior Four loop is going to run
- 03:33
again and again until j is greater than i So
- 03:37
jay starts over at once and we'll print three times
- 03:40
one into space and three times do in the states
- 03:45
hand three times three spaces and three times for in
- 03:48
space but now has five which is greater than i
- 03:51
So we stopped the loop here and continue on with
- 03:53
an empty print line statement and decreasing i yet again
- 03:57
So from here we can totally tell what these loops
- 03:59
are doing and predict what will happen next The lupul
- 04:04
print three six nine and stop it because i will
- 04:07
be three And the local run again printing three six
- 04:18
and three At that point the wild loop will cease
- 04:24
running because i will no longer be greater than zero
- 04:28
Got all that and it looks like the result matches
- 04:31
up with the answer E and yeah that's our answer
- 04:34
and here's your smoke do sure brought to you by 00:04:37.173 --> [endTime] loops Wait not again Allright we're good out No
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
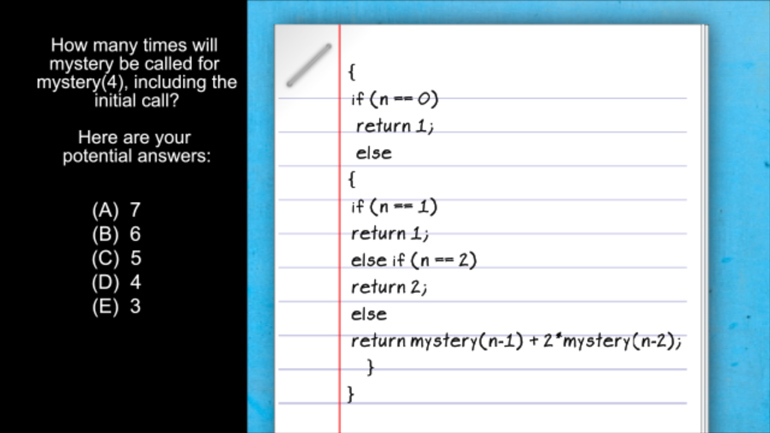
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
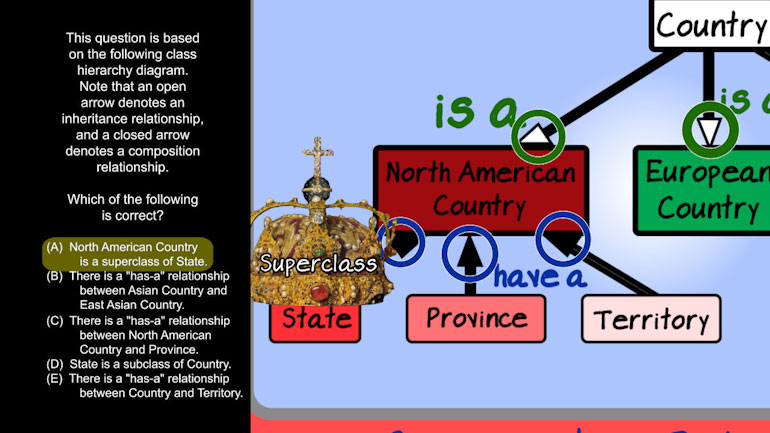
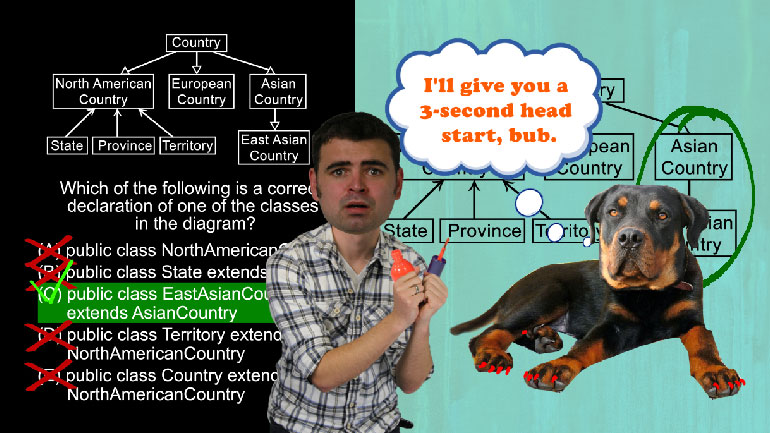
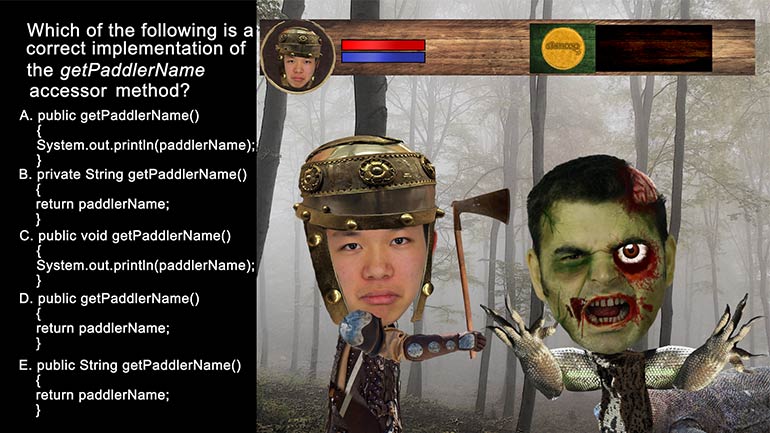
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
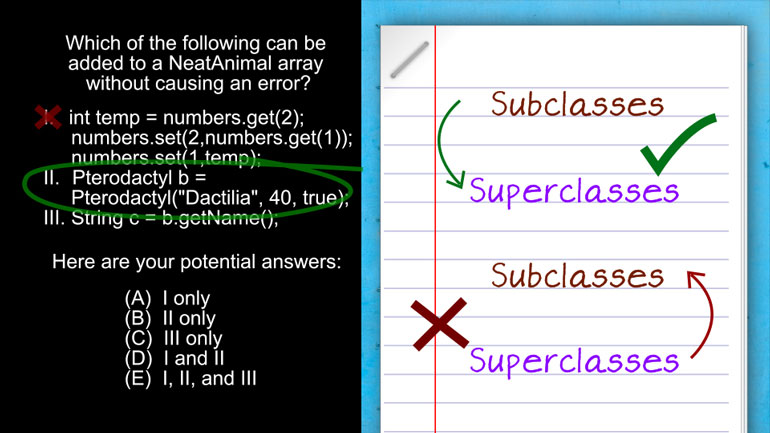
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
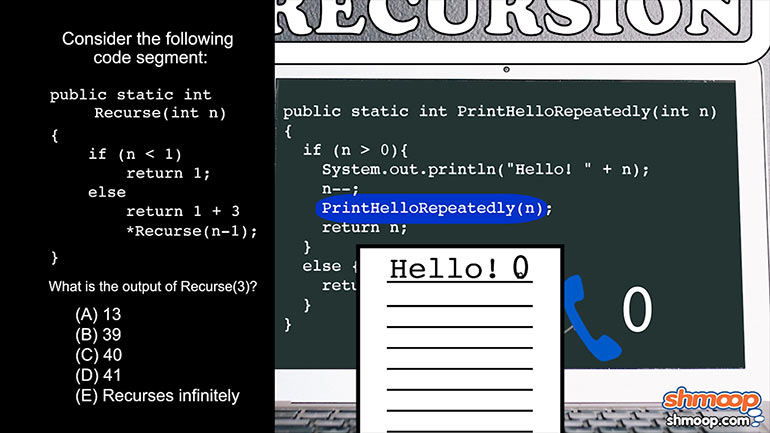
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?