ShmoopTube
Where Monty Python meets your 10th grade teacher.
Search Thousands of Shmoop Videos
Computer Science Videos 112 videos
Just as you move your furniture into a new house before spending the night, you’ve got to spend a little time setting up your environment when yo...
Doubles and ints. At first glance, it may look like this video will be about baseball and football statistics. But they're actually computer scienc...
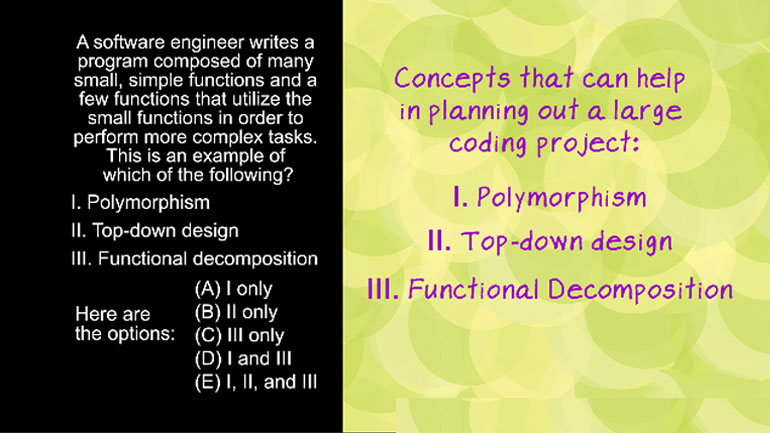
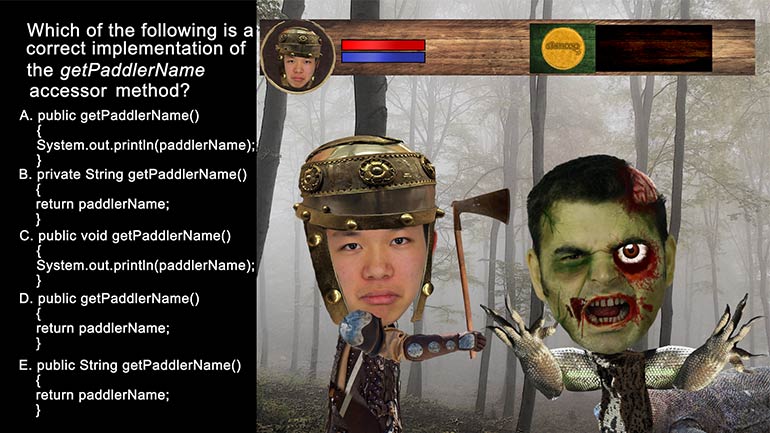
AP Computer Science: Classes and Objects Drill 1, Problem 1. Which of the following is a correct {/* Implementation */} for the isInsect method?
AP Computer Science 1.2 Review of the Basics 207 Views
Share It!
Description:
AP Computer Science: Review of the Basics Drill 1, Problem 2. Which of the following control methods are used in this program?
Transcript
- 00:00
Thank you We sneak And here's your smarts You sure
- 00:06
hated here there's A fibonacci sequence app it's loaded with
- 00:09
ads All right Which of the following control methods are
- 00:13
used in this program Conditional control it Oration incursion All
- 00:18
right And here your potential answers Okay Ready Okay It
Full Transcript
- 00:23
sounds like we're being asked about our understanding of a
- 00:25
few key concepts namely conditional control it oration and rijker
- 00:29
asian let's start by going back over rick Urgent get
- 00:32
it Incursion is one way of implementing a looping mechanism
- 00:37
And you're probably already familiar with the basic idea In
- 00:40
another setting The fibonacci sequence will calculating the fibonacci sequence
- 00:44
by hand is pretty simple Start with one and one
- 00:47
and calculate the next number by adding the two that
- 00:49
came before it doing such a thing in job it
- 00:51
would look a bit like this This fibonacci method takes
- 00:54
an imager as its parameter and returns the number at
- 00:58
that position in the fibonacci sequence calling fibonacci eleven would
- 01:03
end up returning eighty nine for example where we got
- 01:06
that we do out man and here's the magic bit
- 01:08
that makes this a recursive algorithm If are given imager
- 01:11
is greater than the one we're given the some of
- 01:13
the previous vivan aci integer and the one before it
- 01:17
but to calculate those values the method must call itself
- 01:21
However if the imager is one or zero it returns
- 01:24
those values respectively Those air are based cases to keep
- 01:27
our method from becoming infinite It's a lot like that
- 01:30
movie inception except that were actually able to figure out
- 01:33
how the ending works The code snippet given by the
- 01:36
question doesn't feature any riker jh in though there's also
- 01:39
the concept of conditional controls which is to say if
- 01:42
statements none of those here what about federation Oh you
- 01:46
betcha Four loops while lips and do wild loops are
- 01:49
federation statements in java and they worked by wealth iterating
- 01:53
innit aerator and it aerator is just an imager that
- 01:56
ticks upward or downward Each time a loop cycles this
- 01:59
poorly it creates an iterated called i will stop running
- 02:02
when i reaches ten and increment i by one each
- 02:05
time the loop cycle that's exactly what's happening in our
- 02:08
question snip it your answer is to uh no it's 00:02:15.947 --> [endTime] definitely B
Related Videos
AP Computer Science 1.2 GridWorld Case Study and APIs. What is the direction of the actor?
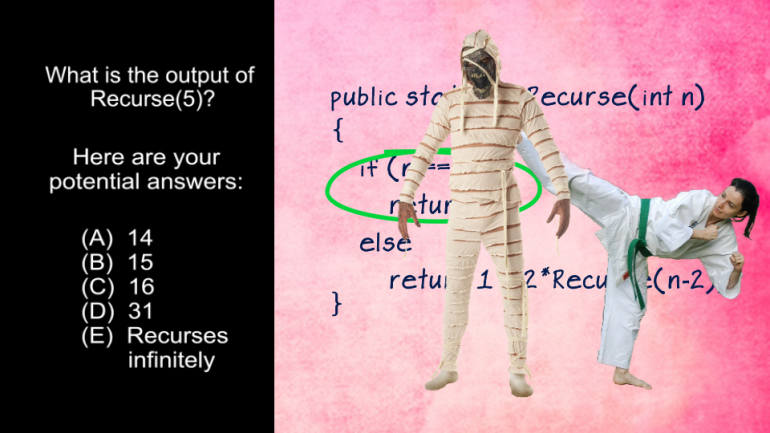
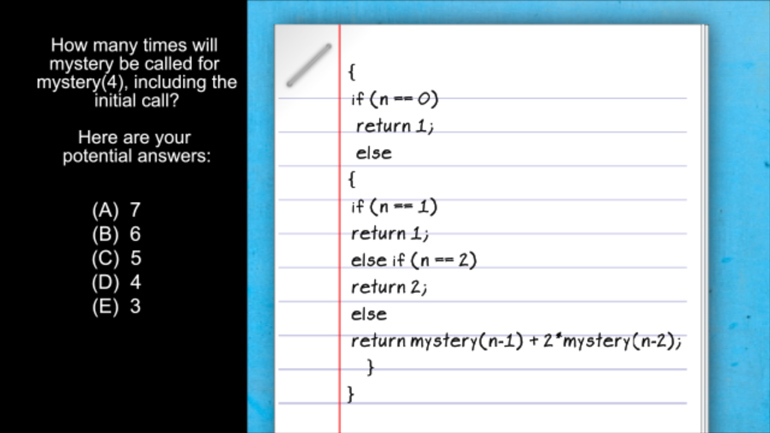
AP Computer Science 1.4 Standard Algorithms. How many times will mystery be called for mystery(n) for n > 1?
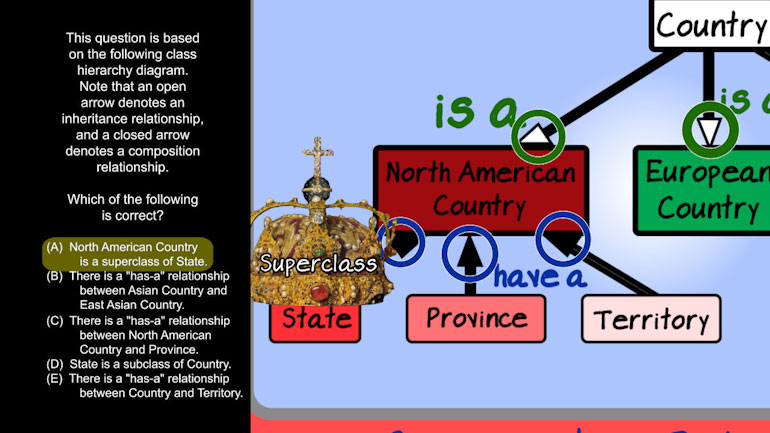
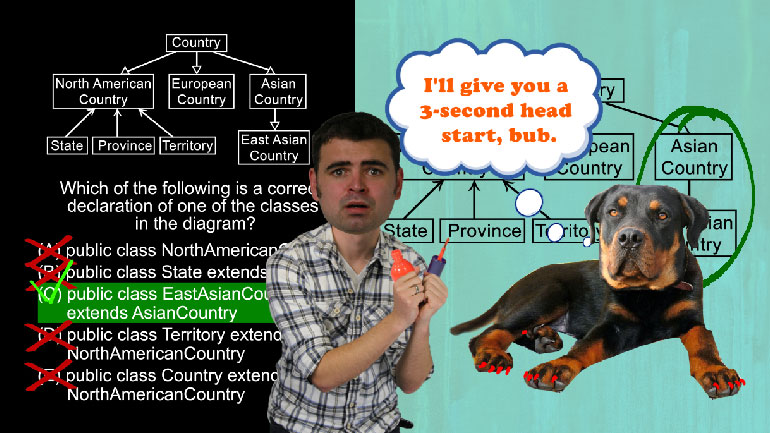
AP Computer Science 2.3 Classes and Objects. Which of the following is correct implementation of the Country class?
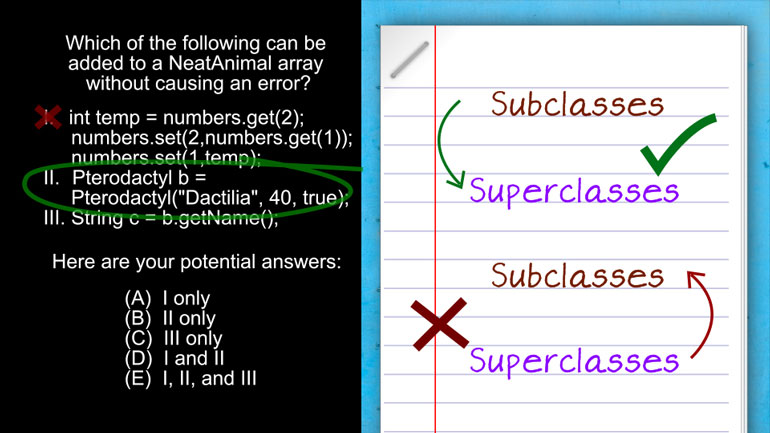
AP Computer Science 3.4 Inheritance, Abstraction, and Polymorphism. Which of the following will satisfy the conditional if statement for boo, str,...
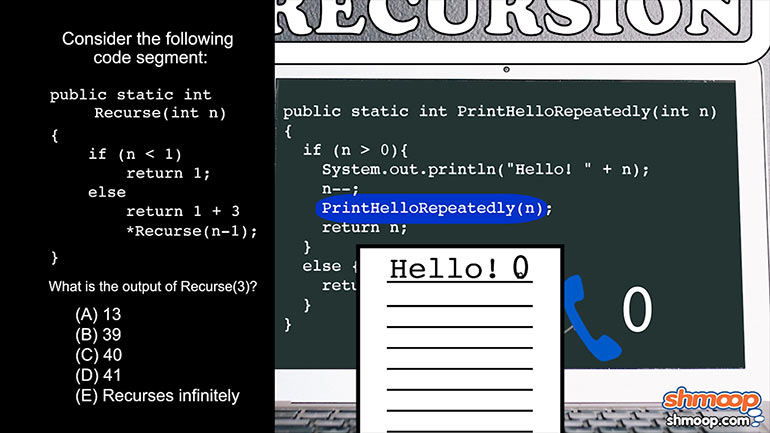
AP Computer Science 4.2 Standard Algorithms. What kind of algorithm is the following?